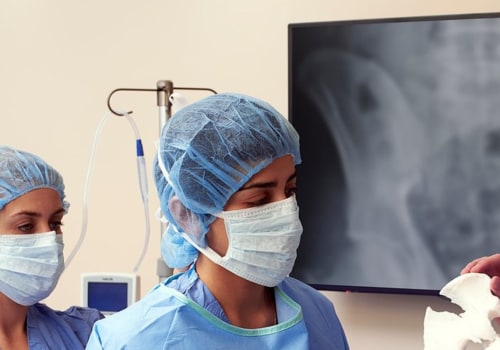
With 3D printing, you can create ergonometric equipment and tools for surgical procedures. These tools reduce discomfort, fatigue and tension during operation, ensuring greater accuracy during treatment. They also reduce the time needed on the operating table. The models allow doctors to understand the anatomy of patients that is difficult to visualize, especially when using minimally invasive techniques.
Models also help to precisely size medical devices. Physicians can also use models to explain an upcoming medical procedure to patients and their families and to communicate surgical steps to their colleagues. Advances in medical 3D printing technology have made enormous contributions to the fields of healthcare. For patients, new therapeutic tools and methods developed through 3D printing can bring new degrees of comfort and personalization to treatment.
For doctors, this newly accessible technology allows for a better understanding of complex cases and provides new tools that can ultimately result in a higher level of care. Orthopedic surgery has also used the use of 3D printed models to plan operations involving a rare or abnormal anatomy. The resulting orthosis, tailor-made and 3D printed, provided Nik with support, comfort and correction precisely where he needed it, helping Nik to finally take his first steps independently. The ease of use and low cost of in-house 3D printing have also revolutionized product development, and many manufacturers of medical tools have adopted this technology to produce completely new medical devices and surgical instruments.
SLA 3D printing offers a wide selection of 3D printing materials, including biocompatible materials, for a variety of medical and dental applications. Before the advent of 3D printers, the main method for manufacturing a single part for prototyping was the use of a numerically computer-controlled machine (CNC). The intended anatomy was 3D printed and used to design devices for pre-surgical nasoalveolar molding of the cleft lip and cleft plate (9). The use of 3D printed surgical guides in orthopedic applications has reduced operating time and reduced intraoperative blood loss. SLA 3D printing offers a wide selection of 3D printing materials, including biocompatible materials, for a variety of medical and dental applications. Before the advent of 3D printers, the main method for manufacturing a single part for prototyping was the use of a numerically computer-controlled machine (CNC). The intended anatomy was 3D printed and used to design devices for pre-surgical nasoalveolar molding of the cleft lip and cleft plate (9). The use of 3D printed surgical guides in orthopedic applications has reduced operating time and reduced intraoperative blood loss.
We believe that this is due to the impressive utility and the wide variety of potential applications of 3D printing, in addition to the reduction in costs. One of the ways in which the medical industry has been improved and improved is through the use of 3D printers. More than 90 percent of the top 50 medical device companies use 3D printing to create accurate prototypes of medical devices, templates and accessories to simplify testing, in addition to directly 3D printing medical devices. 3D printing not only allowed the manufacture of the device, but also a quick delivery to improve the design.
To help reduce costs, some centers have developed procedures in which surgeons practice and plan operations with cheap mannequins that are transplanted with 3D printed models specific to each patient. In hepatobiliary surgery, 3D printing has also been used as a method to study the variants of anatomy before surgery. Jonathan Morris, co-director of the Anatomical Modeling Laboratory and neuroradiologist at the Mayo Clinic, shares the history of 3D printing in medicine and examines real case studies of how radiologists have successfully introduced 3D printing capabilities and programs in hospitals. The wide versatility of SLA is priced slightly higher than that of FDM, but it is still more affordable than all other 3D printing processes.
In addition to the ability to manufacture complex and customized parts, 3D printing in the healthcare sector is best suited for low-volume production, which means that costs will be reduced and efficiency will increase...